
This conclusion is not based merely on the marginal distributions because it relies on independence. Consequently it is itself normally distributed.

Notice that the part over the underbrace is a sum of independent random variables each of which is normally distributed. True or False: If the sampled population is a normal distribution, then the sampling distribution of X-bar may not be normal for a small sample size. The optional weights parameter sets weights for each of the x values.discreteTrue is needed to have a bar for each x value. A statistics sampling distribution is just the distribution of all possible values the estimate could take, over all possible samples of a given size drawn from the population of interest. Impact of shape of distribution on measures of. If a random variable X is normally distributed, what. The extended and improved versions are now called histplot (histogram with optional kde ), kdeplot (for just a kde) and displot (creates subplots). What youre referring to as 'variance' is generally called standard error, the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of the statistic. When the mean is calculated on a distribution from a sample it is indicated by the symbol x (pronounced X-bar). The standard deviation of the sampling distribution of x-bar is called the standard error of the mean. And those conclusions are not based simply on the marginal distributions. True or False: In the sampling distribution of the mean for a large sample size, it has a normal distribution with the same mean as the population but with a smaller standard deviation. First off, note that distplot has been depreciated in Seaborn 0.11. Confidence intervals can be calculated using the Confidence Interval Calculator.Nobody is making assumptions in this matter rather, someone is drawing conclusions. Since any linear combination of normal variables is also normal, the sample mean X bar X X is also normally distributed (assuming that each X i Xi Xi is. Sampling distributions form the theoretical foundations for more advanced statistical inferennce, such as confidence intervals. Probabilities for continuous distributions can be calculated using the Continuous Distribution Calculator. The normal distribution is one example of a continuous probability distribution. If the sample size is large enough, the sampling distribution of the sample mean approximates a normal distribution. Let X 1, X 2,, X n be a random sample of. In doing so, well discover the major implications of the theorem that we learned on the previous page. To find the distribution of x¯ x ¯, you need to use that if X N(1,21) X N ( 1, 1 2) and Y N(2. This naturally generalizes to linear combinations of n n independent random variables. The sampling distribution of x-bar has standard deviation n even if the population is not normally distributed. V a r ( a X + b Y) a 2 V a r ( X) + b 2 V a r ( Y). In a random sample, the elements are chosen independently and come from the same population. Well finally accomplish what we set out to do in this lesson, namely to determine the theoretical mean and variance of the continuous random variable X ¯. and if furthermore X X is independent of Y Y then. When sampling from an infinite population, a random sample is preferred. In a simple random sample, each element from the population has the same probability of being selected. When sampling from a finite population, a simple random sample is preferred. The sampling procedure depends on whether you're sampling from a finite or infinite population. Using a subscript that matches the random variable. Sampling is the process of selecting the elements of a sample from a population. Suppose X is a random variable with a distribution that may be known or unknown (it can be any distribution). Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like x-bar is the value of the mean of the sampling distribution of x-bar., The standard deviation of the population is less than the standard deviation of the sampling distribution of x-bar., The sampling distribution of x-bar is always taller and skinnier than the population.
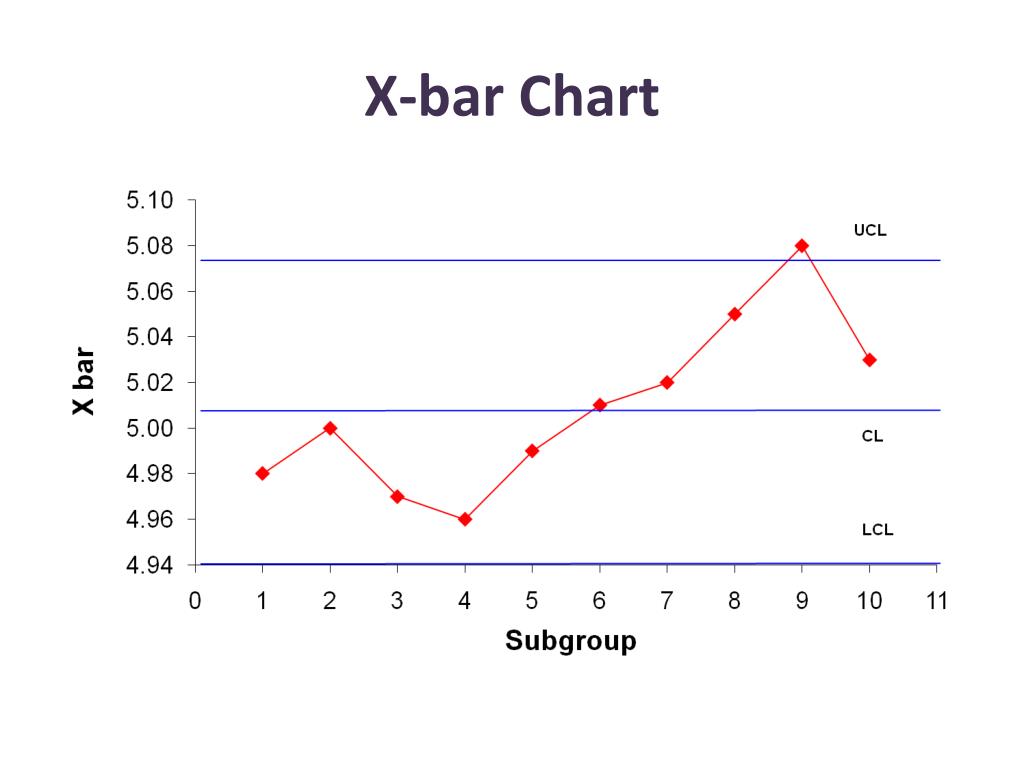
So, for example, the sampling distribution of the sample mean ($\bar$
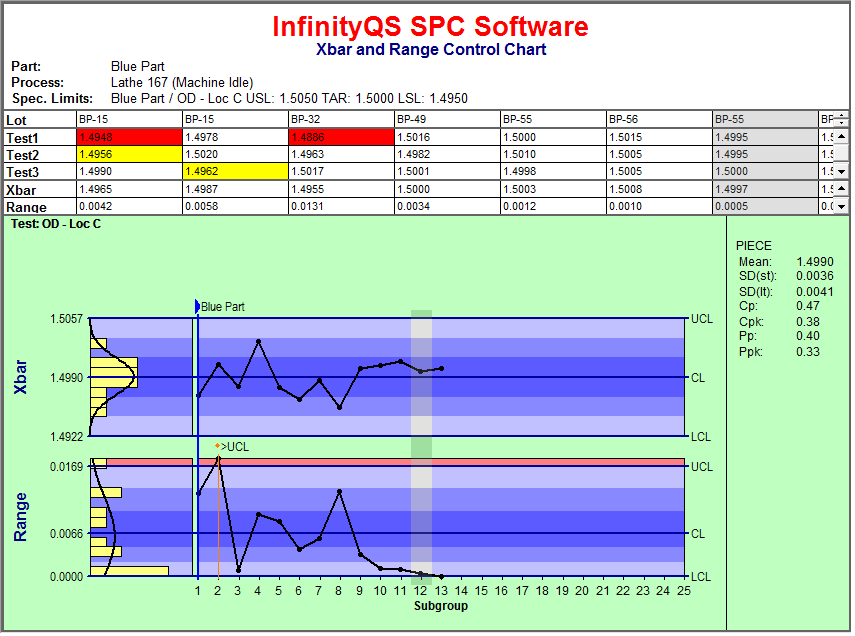
A sampling distribution is the probability distribution of a sample statistic.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
